Since Thevenin's and Norton's Theorems are two equally valid methods of reducing a complex network down to something simpler to analyze,Consider the figure below which schematically represents the two-terminal network of constant emf's and resistances; a high-resistance voltmeter, connected to the accessible terminals, will indicate the so called open circuit voltage voc. If an extremely low-resistance ammeter is next connected to the same terminals, as in fig.(b), which is so called the short-circuit current iscwill be measured.
 |
| Test circuits for Thevenin's Theorem |
Now the two quantities determined above may be used to represent an equivalent simple network consisting of the single resistance RTH, which is equal to voc/isc. If the resistor RL is connected to the two terminals, the load current of the circuit will be
IL = voc / RTH+RL---------------1
The
analysis leading to the equation no.1 above was first proposed by M.L. Thevenin
the latter part of the nineteenth century, and has been recognized as an
important principle in electric circuit theory. His theory was stated as
follows: In any two-terminal network of fixed resistances and constant sources
of emf, the current in the load resistor connected to the output terminals is
equal to the current that would exist in the same resistor if it were connected
in series with (a) a simple emf whose voltage is measured at the open-circuited
network terminals and (b) a simple resistance whose magnitude is that of the
network looking back from the two terminals into the network with all sources
of emf replaced by their internal resistances.
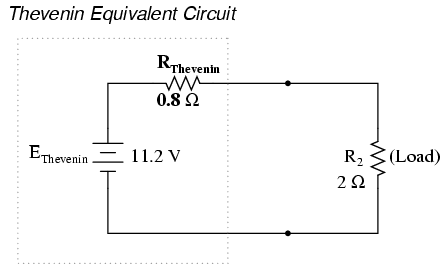 Thevenine Equivalent Circuit
Thevenine Equivalent Circuit








0 comments:
Post a Comment